Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is essentially the most frequent and aggressive major mind tumor in adults.
Regardless of in depth remedy the prognosis for GBM sufferers stays poor and the extraordinary remedy resistance has been attributed to intertumoral heterogeneity of glioblastoma.
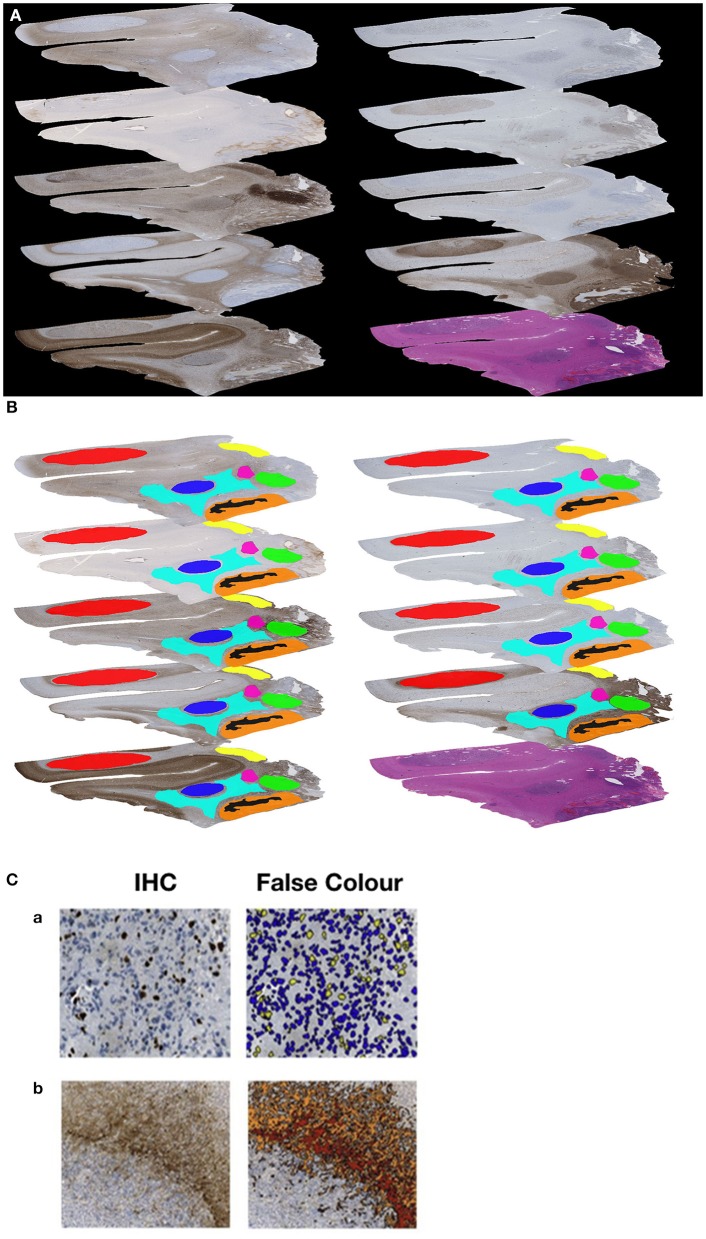
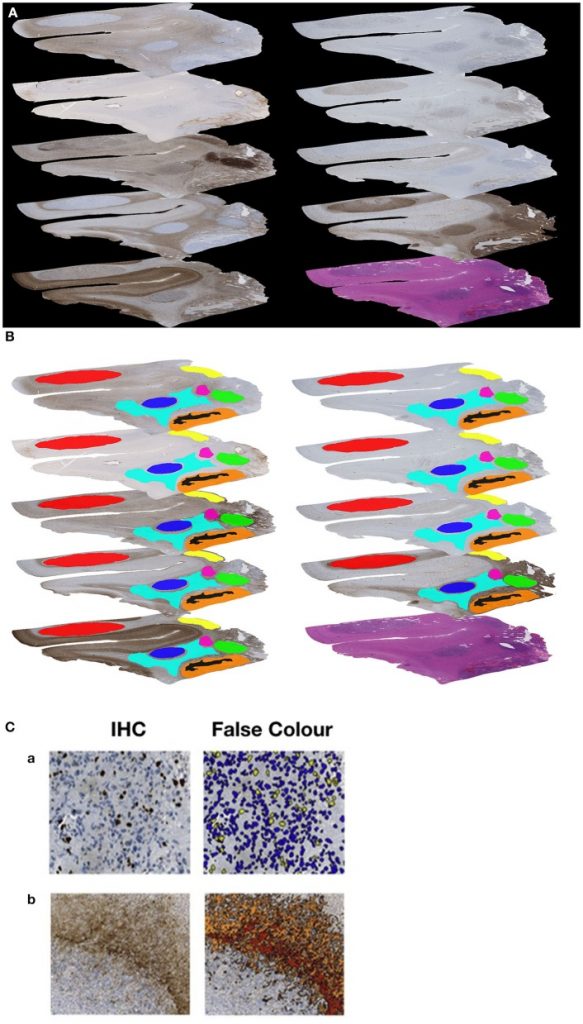
Completely different prognostic related GBM tumor subtypes have been recognized primarily based on their molecular profile. This strategy, nonetheless, neglects the heterogeneity inside particular person tumors, that’s, the intratumoral heterogeneity. Right here, we detected the regional immunoreactivity by immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence utilizing 9 completely different markers on resected GBM specimens (IDH wildtype, WHO grade IV).
We discovered repetitive expression profiles, that may very well be labeled into clusters. These clusters may then be assigned to 5 pathophysiologically related teams that mirror the beforehand described subclasses of GBM, together with mesenchymal, classical, and proneural subtype.
Our knowledge point out the presence of tumor differentiations and tumor subclasses that happen inside particular person tumors, and would possibly subsequently contribute to develop tailored, individual-based therapies.
Diagnostic Accuracy of Immunohistochemistry for Mismatch Restore Proteins as Surrogate of Microsatellite Instability Molecular Testing in Endometrial Most cancers.
Microsatellite instability (MSI) defines one of many 4 molecular teams of endometrial carcinoma recognized by The Most cancers Genome Atlas (TCGA). Immunohistochemistry for mismatch restore (MMR) proteins (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2) has been proposed as a extensively relevant approach to establish this group within the frequent observe.
Nonetheless, the diagnostic accuracy of such strategy has by no means been calculated. We aimed to evaluate: 1) the diagnostic accuracy of MMR proteins immunohistochemistry as surrogate of MSI molecular testing in endometrial carcinoma;
2) whether or not a mix of solely two MMR proteins could also be used as a nonetheless cheaper take a look at. A scientific evaluate and meta-analysis of was carried out by looking out digital databases from their inception to September 2019.
All research assessing endometrial carcinoma with each MMR proteins immunohistochemistry and MSI molecular testing have been included. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed as sensitivity, specificity, constructive and unfavorable probability ratios (LR+, LR-), diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) and space below the curve (AUC) on SROC curves.
A subgroup evaluation was carried out for a mix of solely two MMR proteins (MLH1-MSH2 vs MSH6-PMS2). Ten research with 3097 sufferers have been included. Out of those, 1110 have been appropriate for the meta-analysis. Immunohistochemistry for all of the 4 MMR proteins confirmed sensitivity = 0.96, specificity = 0.95, LR + =17.7, LR- = 0.05, DOR = 429.77, and excessive diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.988).
The mixture of MLH1 and MSH2 confirmed sensitivity = 0.88, specificity = 0.96, LR + =22.36, LR- = 0.15, DOR = 200.69, and excessive diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.9838). The mixture of MSH6 and PMS2 confirmed the identical outcomes as the whole panel of 4 MMR proteins.
In conclusion, MMR proteins immunohistochemistry is a extremely correct surrogate of MSI molecular testing in endometrial carcinoma. A mix of MSH6 and PMS2 might permit lowering the associated fee with out lower within the diagnostic accuracy.